What is the process of casting products using plastic injection molding?
The process of manufacturing products using plastic injection molding is the most commonly used method to produce plastic parts, products, components, and details. There are numerous products manufactured using injection molding, varying greatly in size, complexity, and application. The injection molding process requires the use of an injection molding machine, raw plastic material, and a mold. The plastic is melted in the injection molding machine and then injected into the mold, where it cools and solidifies into the desired product. The steps in this process are described in more detail in the following section.
Injection molding is used to produce thin-walled plastic parts for many applications, with one of the most common types being plastic casings. Plastic casings are a frame with thin walls, often requiring ribs (spines) to increase rigidity. These casings are used in various products including household appliances, consumer electronics, power tools, and automotive control panels. Other common thin-walled products include various types of open containers, such as buckets. Injection molding is also used to produce everyday items like toothbrushes or small plastic toys. Many medical devices, including valves and syringes, are also manufactured using the injection molding method.
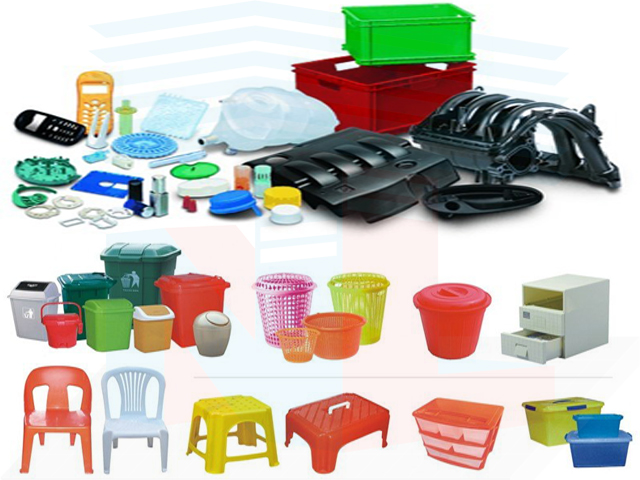

Products that use the injection molding method
Products that utilize the injection molding method
Plastic Injection Molding Machines :
There are several ways to classify pressure casting machines, but common methods include the following:
- By clamping force: Types range from 50 to 8000 tons.
- By the maximum shot weight of the product: 1, 5, 8, 10, to 120 oz.
- By the type of platen or screw.
- Screw type.
- Whether the screw is horizontal or vertical.
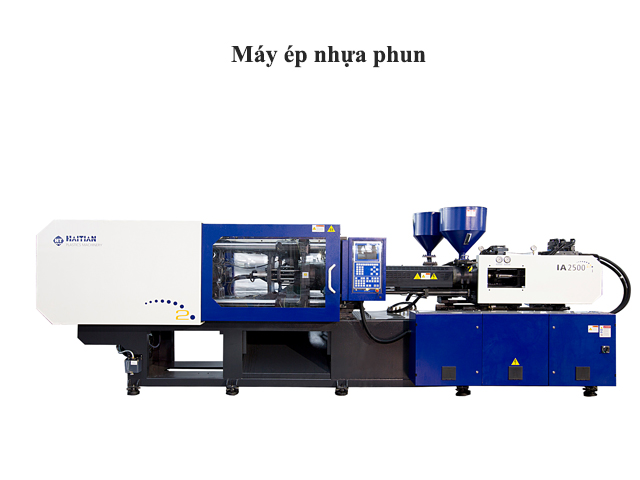

Structure of a plastic injection molding machine
A plastic injection molding machine consists of the following main components: Clamp system, mold, injection system, hydraulic system, control system.
Clamp system
It functions to open and close the mold while also assisting in moving the mold components and generating sufficient force to hold the mold during the filling process and eject the product from the mold. The movement of this assembly is translational, so any mechanism that produces this movement can be applied.
Common types of clamp assemblies include:
Mechanical clamp assembly.
Hydraulic clamp assembly.
Mechanical-hydraulic combined clamp assembly.
Mold
It consists of two basic components: the fixed half and the movable half. The movable half typically carries the core of the mold, while the fixed half usually carries the cavity of the mold. Cooling systems and plastic flow channels are arranged in the mold plates. Additionally, there are connecting rods and other components such as the heating system… I will explain in detail in the plastic injection mold section.
Injection System
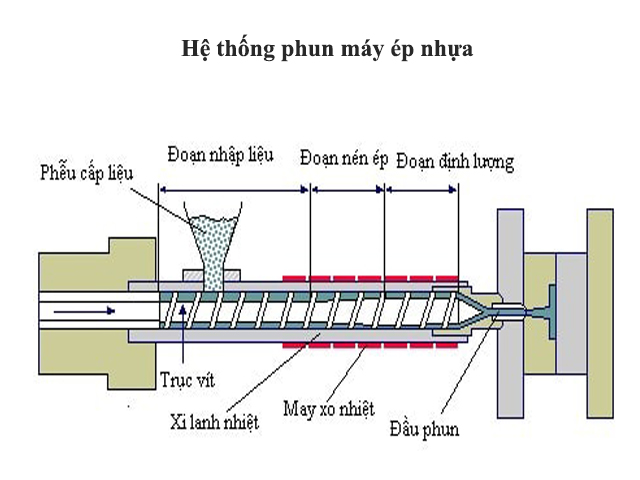
The injection system consists of 3 main components: the material hopper, the heating cylinder, the screw, screw head, and the nozzle.
Material hopper: Plastic resin is supplied in the form of small pellets. The material hopper serves to contain these material pellets. These small material pellets move from the hopper opening into the heating cylinder.
Heating cylinder: The heating cylinder heats the material, causing it to melt and become liquid. It is heated by heating bands.
Screw: The screw consists of 3 segments:
Feeding section: Located near the material hopper, it is used to transfer raw material forward. At the end of this section, the material becomes soft and begins to flow (50%L).
Compression section: In the middle of the screw, it is used to compress the liquid material (25%L).
Metering section: Mixes and homogenizes the material before injection into the mold.
Nozzle: This is the part between the cylinder head and the nozzle tip of the mold. The nozzle must have a suitable shape for material flow and must be tightly attached to the nozzle tip during the injection process. The nozzle hole should be smaller than the nozzle tip hole in the mold. The nozzle can be interchangeable and have its own heating ring. Due to different plastic characteristics, the nozzle also has different structures to ensure the best injection into the mold.
Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system is responsible for providing energy to open and close the mold, maintaining tight clamping force, rotating the screw, and providing force for ejector pins to separate the mold. The hydraulic system includes pumps, valves, hydraulic motors, piping systems, and reservoirs.
Control System
The control system is responsible for ensuring stable and repeatable operation of the machine. It displays and controls various parameters of the injection molding process, such as temperature, pressure, injection speed, position and speed of the screw rotation, and position of the hydraulic system. The control process directly affects the final quality of the product and its economic viability.
The plastic injection molding process
The plastic injection molding process typically has a very short processing cycle, ranging from 2 seconds to 2 minutes, and consists of the following four stages:
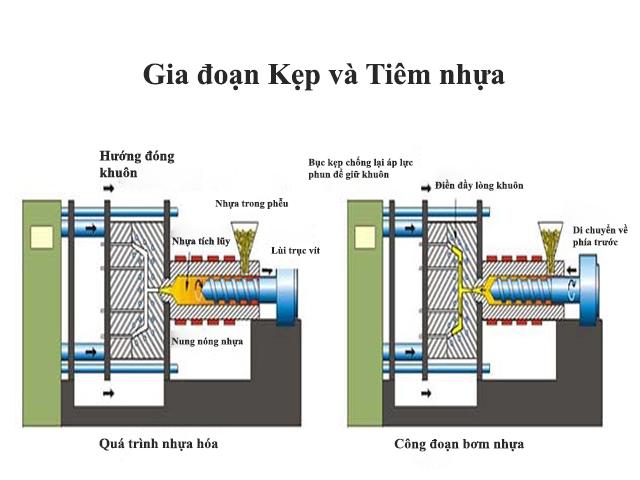
Clamping – Before injecting material into the mold, the two mold halves must first be tightly closed by the clamping unit. Each mold half is attached to the injection molding machine, with one half allowed to slide. The hydraulic clamping unit pushes the two mold halves together and applies enough force to keep the mold tightly closed while the material is injected. The time required to close and clamp the mold depends on the machine – larger machines (those with higher clamping force) will require more time. This time can be estimated from the machine’s dry cycle time.
Injection – Raw plastic material, usually in the form of pellets, is fed into the injection molding machine and advances towards the mold through the injection unit. During this process, the material is melted by heat and pressure. The molten plastic is then injected into the mold very quickly, forming pressure packs and holding the material. The amount of material injected is called the shot. The injection time is very difficult to calculate accurately due to the complex flow of plastic and changes within the mold. However, the injection time can be estimated based on the shot volume, injection pressure, and injection power.
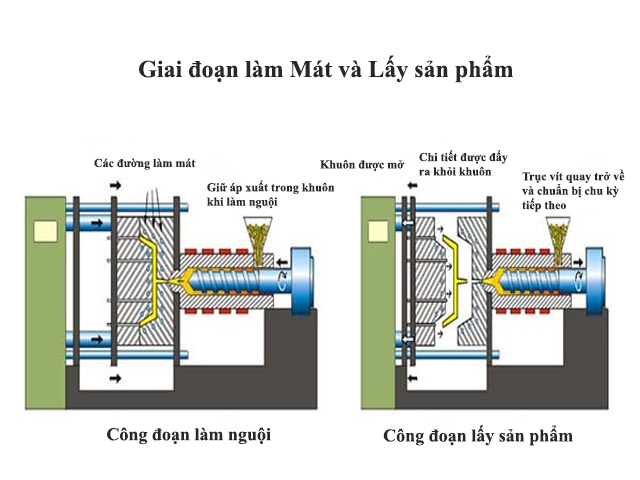
Cooling – The molten plastic inside the mold begins to cool as soon as it comes into contact with the inner surface of the mold. As the plastic cools, it solidifies into the desired shape. However, during the cooling process, some shrinkage of the product may occur. The mold cannot be opened until the necessary cooling time has elapsed. The cooling time can be estimated from certain thermal properties of the plastic and the maximum wall thickness of the product.
Ejection – Once enough time has passed, the cooled part can be ejected from the mold using an ejection system, attached to the rear half of the mold. When the mold is opened, a mechanism is used to push the product out of the mold. After the part is ejected, the mold can be closed again to carry out the next cycle.
Plastic Injection Mold
The injection molding process utilizes molds, typically made of steel or aluminum, as customized tools. The mold consists of multiple components but can be divided into two halves. Each half is mounted inside the injection molding machine, with the rear half allowed to slide so that the mold can be opened and closed along the mold’s parting line. The two main components of the mold are the core and cavity. When the mold is closed, the space between the core and cavity forms the part cavity, which will be filled with molten plastic and then cooled to produce the desired product.
Fixed half (Cavity mold): This part remains stationary throughout the entire injection molding process. It is tightly mounted to the stationary side of the injection molding machine and is connected to the machine’s plastic injection nozzle system to deliver molten plastic into the mold cavity through the injection nozzles and runners.
Moving half (Core mold): This part is responsible for closing the mold to inject the product and opening the mold to retrieve the product. The moving half is attached to the moving side of the injection molding machine and connected to the mold ejection system to push the product out through the ejector pins designed within the mold.
Above are the details related to the injection molding process. With the information provided above, you must have gained useful knowledge about the injection molding process and its applications in daily life.
ATT Vietnam is also a specialized agent providing high-quality and competitively priced plastic injection molding products. For more detailed information about the plastic injection molding process, please feel free to contact us for further consultation.
Address: Lot 32 Bai Say, Zone Cau Do 5, Ha Cau Ward, Ha Dong District, Ha Noi, Vietnam.
Factory: Lot CN6, Thach That – Quoc Oai Industrial Zone, Thach That District, Hanoi, Vietnam.
Email: [email protected]
Mobile: +84 2432 003 219
Hotline: +84 979 011 304 (Zalo/Whatsapp/Telegram)

